This simple science demonstration is a fantastic way to learn about volcanoes, tectonic plates and convection currents.
Volcanoes are mostly found on tectonic plate boundaries because the movement of tectonic plates allows magma to reach the surface. The Ring of Fire around the Pacific Plate is home to around 75% of the world’s volcanoes!
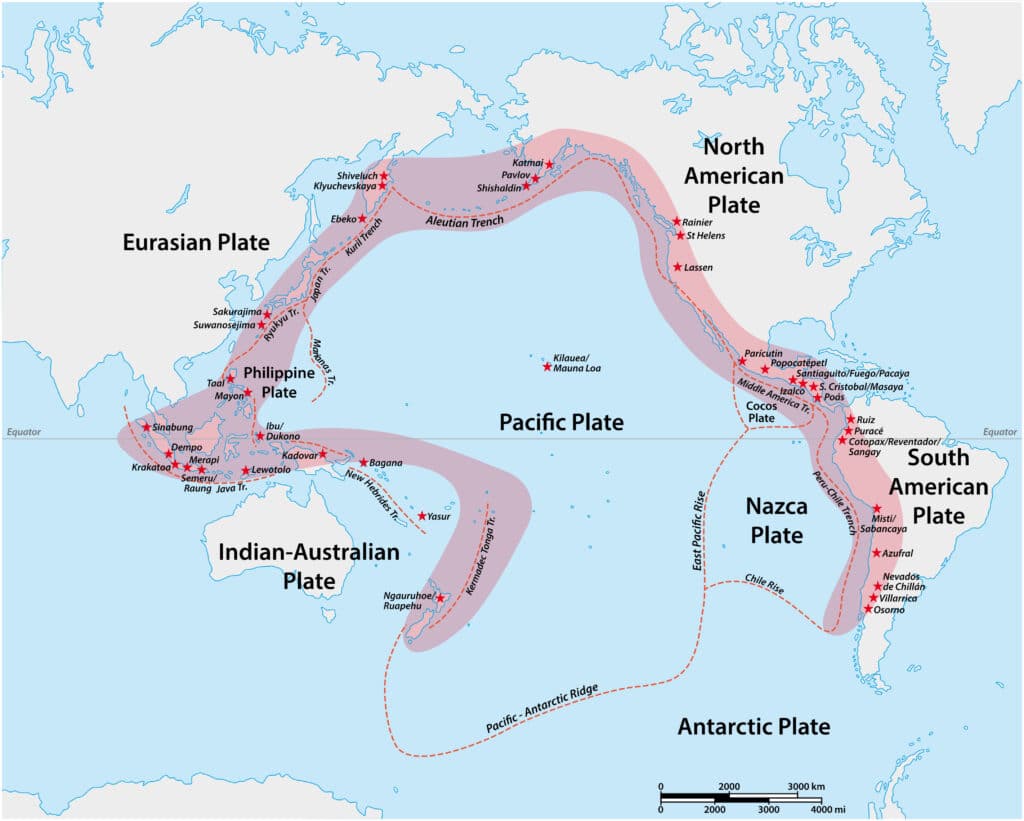
Volcanoes form in three areas:
- constructive plate boundaries
- destructive play boundaries
All three settings are places where magma is able to escape through gaps in the Earth’s crust.
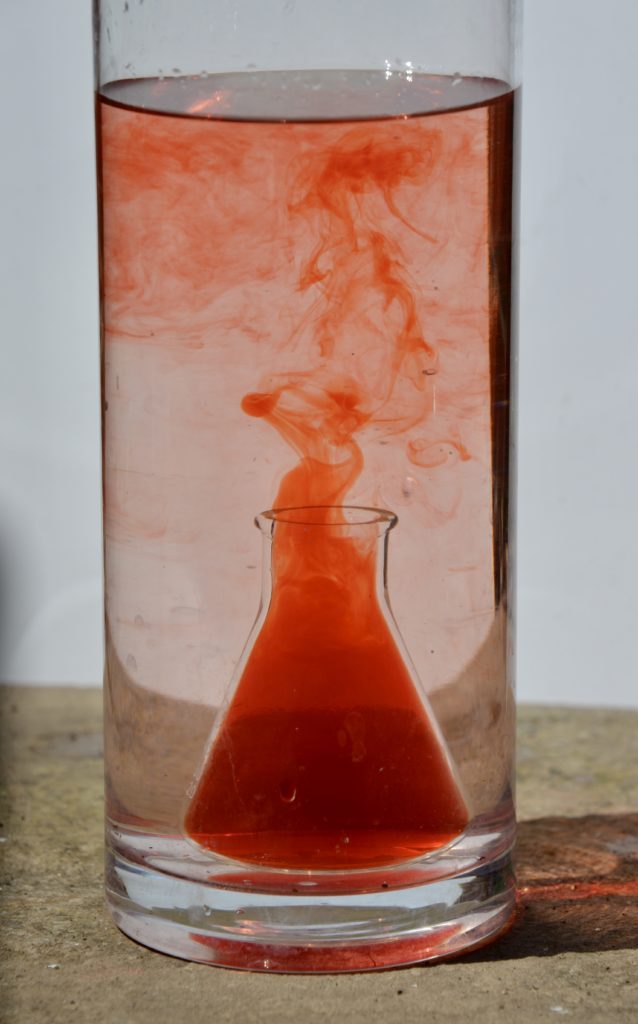
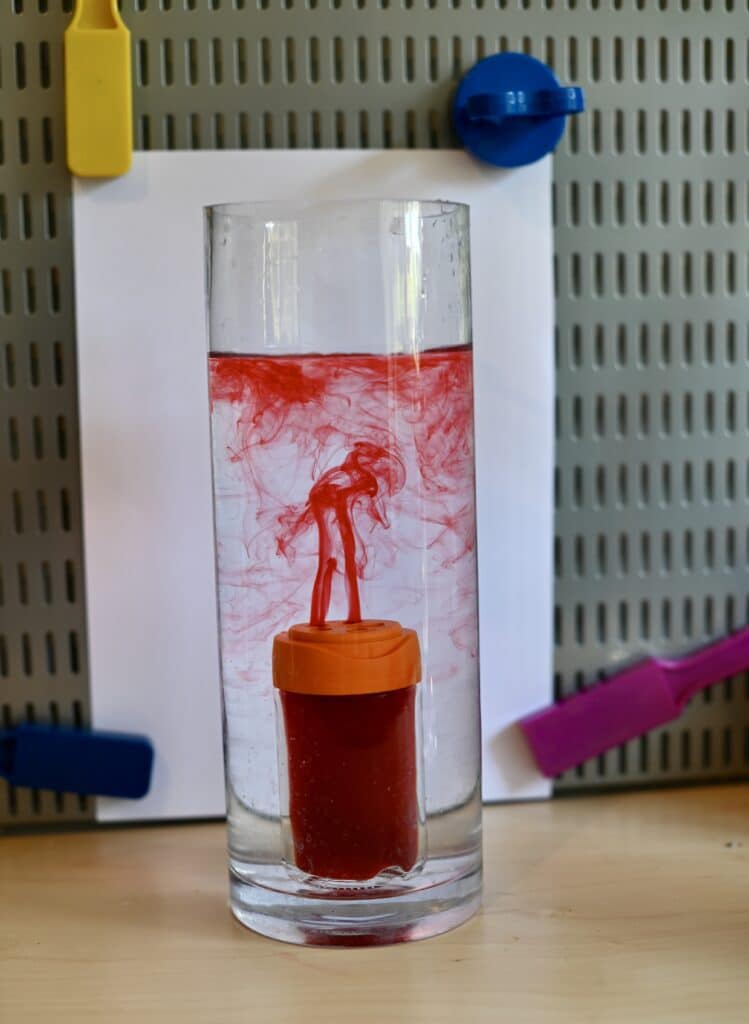
This underwater volcano science demonstration shows how convection currents work. Convection currents allow hot magma to rise up through the mantle to the Earth’s crust.
How to make an underwater volcano
You’ll need
A large jar
Cold water
Hot water
Food colouring
Small conical flask or spice jar
Instructions for an Underwater Volcano
Fill the large jar, about ¾ full, with cold water.
Carefully ( ask an adult to help ) fill the smaller container close to the top with hot water and add a few drops of food colouring.
Carefully lower the small container into the large jar. Watch as the warm, coloured water rises up into the cooler water above.
If you’re using a spice jar with small holes, you’ll need to shake the jar a little to allow any air bubbles to escape.

What is a convection current?
A convection current is how heat rises and falls in liquids and gases. When a liquid or gas is heated, the particles move faster than when they are cold. The space between particles increases, making the density decrease. The warm, less dense liquid or gas rises upwards, and cooler, denser liquids or gases fill the space. This leads to a convection current as the process is repeated over and over again.


Convection currents and plate tectonics
Convection currents play an important role in the movement of magma in the Earth’s crust and mantle layers. Heat from the Earth’s core warms the magma closest to it. The hot magma rises up through the mantle, cools as it gets closer to the crust and sinks again. This is a convection current. As the magma sinks, it can move tectonic plates across the surface of the Earth.
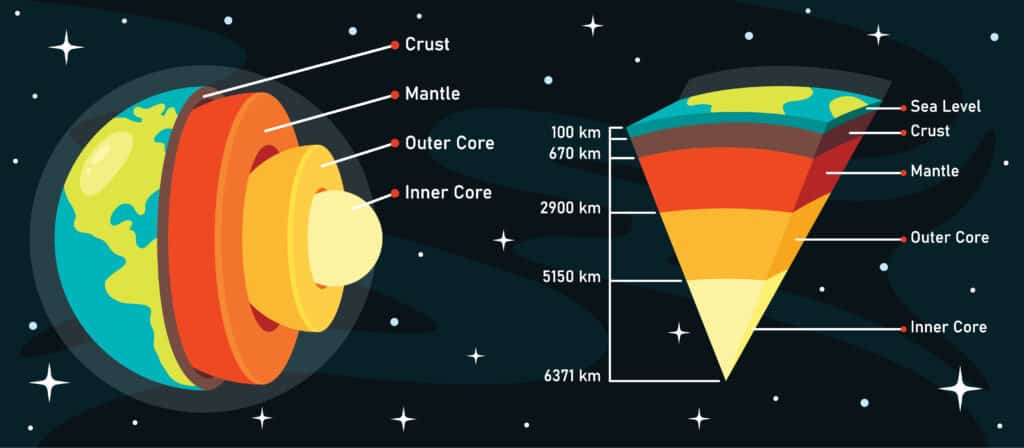
This movement of tectonic plates leads to cracks or fissures in the ground, allowing magma to reach the Earth’s surface, and is why most volcanoes are found at plate boundaries.
Tectonic Plate Boundaries
Constructive plate boundaries
Constructive plate boundaries ( divergent ) form where convection currents move plates apart. As the plates move apart, magma rises up from the earth’s mantle layer to fill the gap. The magma cools at the surface, forming igneous rock. The process eventually leads to the formation of ridges and rifts. If magma erupts onto the surface, shield volcanoes can form.
If this process happens between continental plates, it creates deep, wide valleys on land. When it occurs between oceanic plates, it leads to a mid-ocean ridge. Examples of mid-ocean ridges include the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge, East Pacific Rise and the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Volcanoes are often found along mid-ocean ridges.
This type of plate boundary is also called divergent.
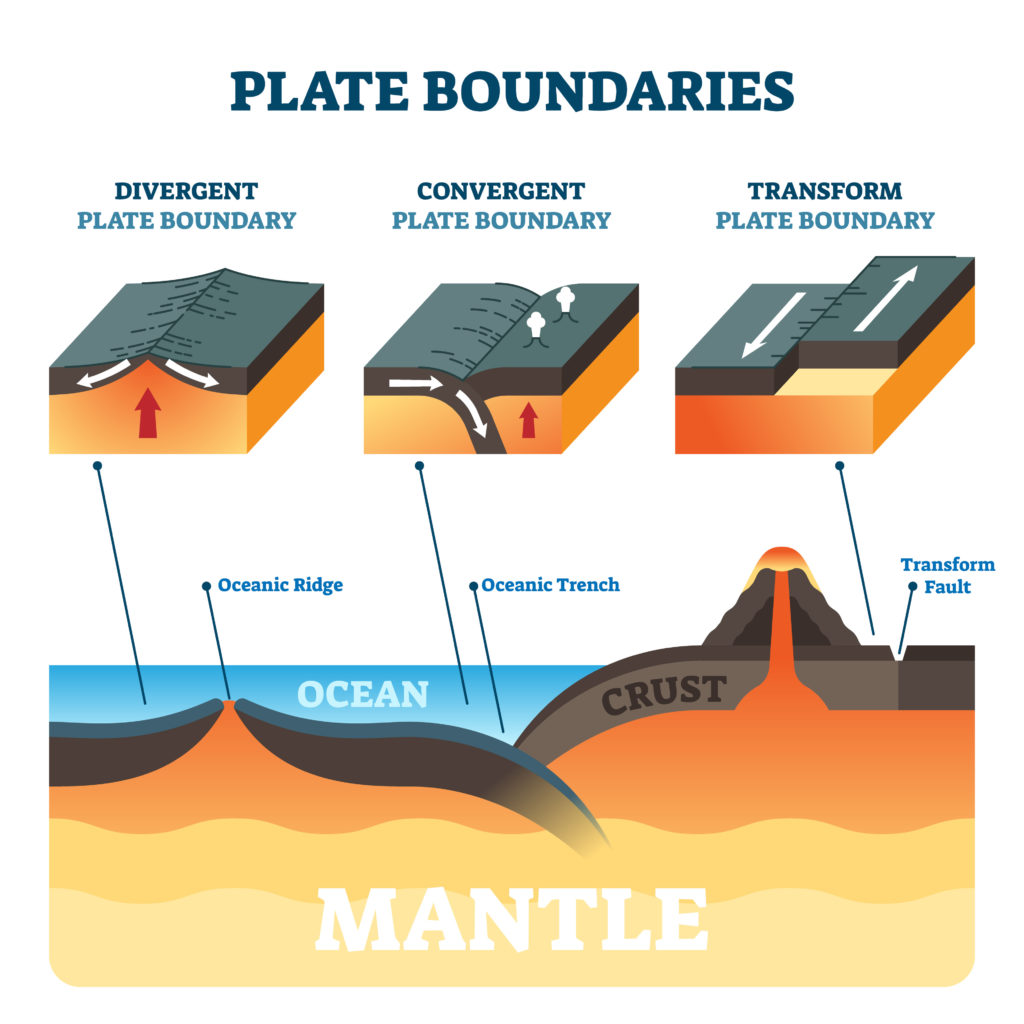
Destructive plate boundaries
Destructive plate boundaries ( convergent ) form where convection currents push tectonic plates together. There are three types of destructive plate boundaries.
- oceanic plate and oceanic plate
- oceanic plate and continental plate
- continental plate and continental plate
Continental and oceanic
Oceanic plates are denser than continental plates. This means that the oceanic plate is forced under the continental plate when they move towards each other. This is called subduction. Oceanic trenches, for example, the Mariana Trench, form when an oceanic plate is forced down under a continental plate. The oceanic plate melts due to friction and heat from inside the Earth to form magma, causing earthquakes. This is known as a subduction zone.
Magma collects in a magma chamber, which then rises up through cracks in the continental crust. If enough pressure builds up, volcanic eruptions can occur, creating volcanoes.
Oceanic plate and oceanic plate
When two oceanic plates collide, the densest plate is pushed down, leading to subduction. The subducted plate melts, creating magma. When the magma comes into contact with the ocean, it cools quickly to form a chain of volcanoes called an island arc.
Continental plate and continental plate
When two continental plates collide, they don’t subduct. Instead, the plates are forced upwards, creating mountains. The collisions can cause earthquakes but not volcanoes.
This type of plate boundary is also called convergent.
Transform plate boundaries
A transform ( or conservative ) boundary is where tectonic plates move past each other. Volcanoes aren’t usually found at this type of plate boundary. The San Andreas Fault, which runs through most of California, is an example of this type of plate boundary.
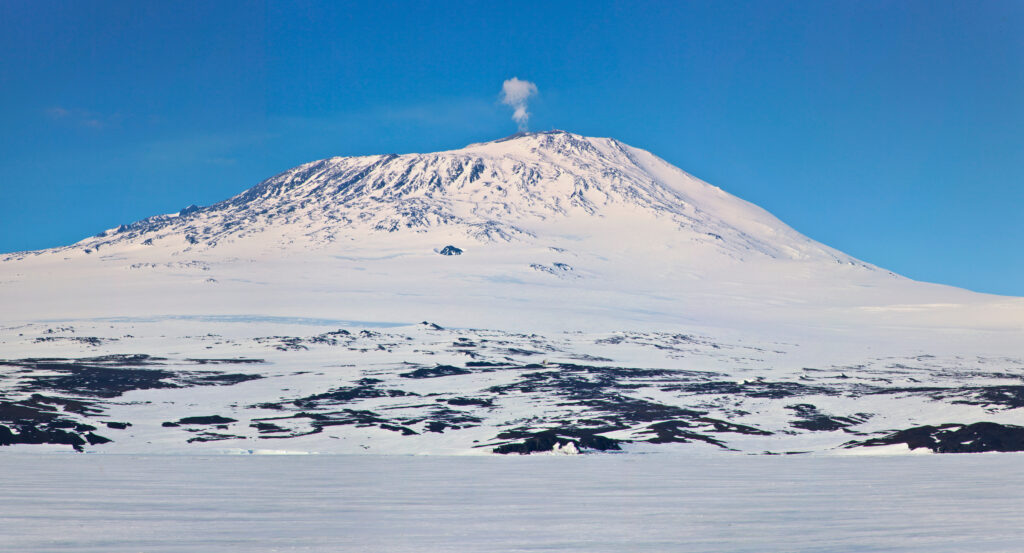
Hot Spots
Hot spots are areas where heat from superheated magma causes the crust above to melt and thin. This allows magma to escape to the surface, forming a volcano. These types of volcanoes are called shield volcanoes. They are flatter than other types of volcanoes.
Mount Erebus in Antarctica is an example of this type of volcano.

More real-life examples of convection currents
Radiators and fires
Hot air rises from heat sources such as fires or radiators. When air near a fire or radiator is heated, it expands, becomes less dense and rises upwards. Cooler, denser air replaces the warm air, which is then heated, becomes less dense and rises. The process continues transferring heat around the room containing the heat source.
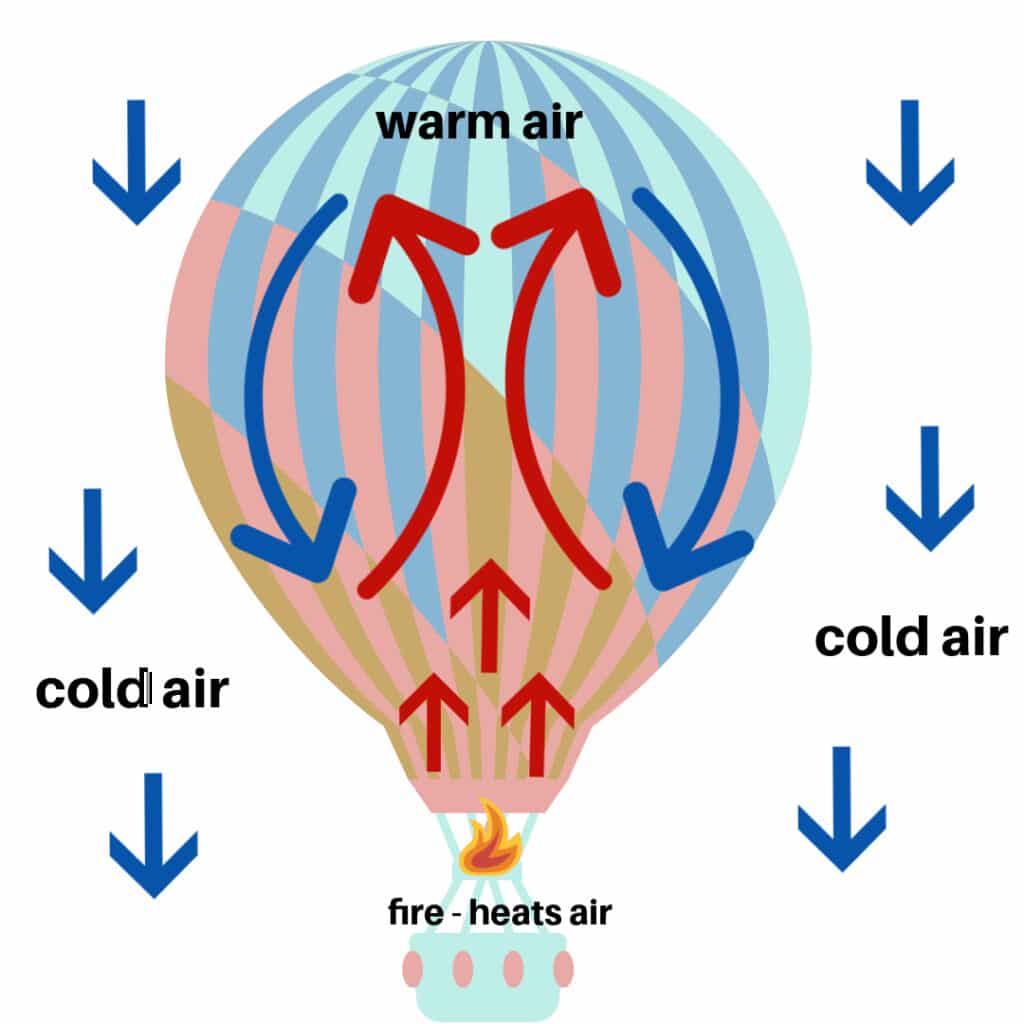
Hot Air Balloons
A convection current heats the air inside the balloon, making the warm air inside the balloon less dense than the cooler air on the outside. This causes the hot air balloon to rise upwards.
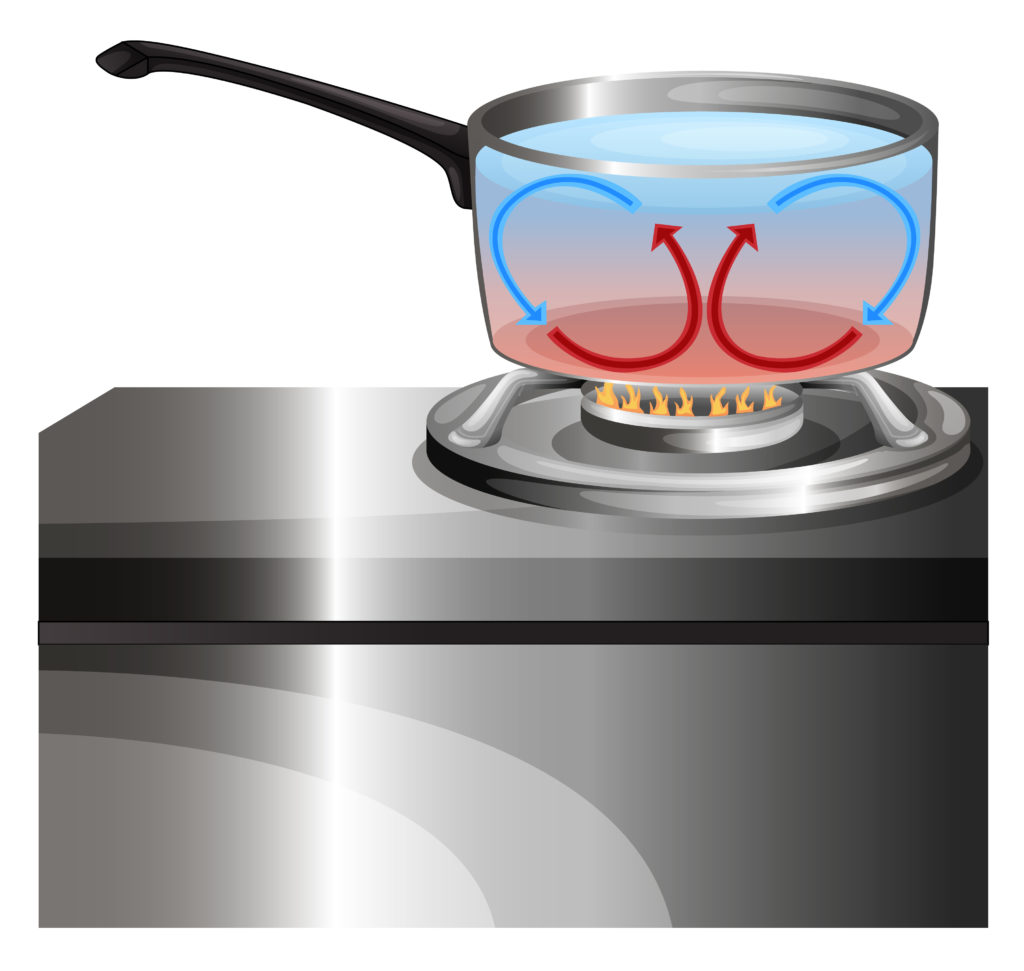
Heating water in a pan
Heating water in a pan is another real-life example of a convection current.

Convection currents also cause sea breezes and most other winds.

More volcano science activities for kids
Make a model seismometer to find out how scientists detect earthquakes.
Learn about tectonic plates with an orange.
Create a playdough model of the Earth’s different layers.
Make a baking soda volcano.
Read about recent volcano activity around the world with NASA.
Science concepts
Convection currents
Tectonic plates
Seismometer
Last Updated on May 24, 2024 by Emma Vanstone


