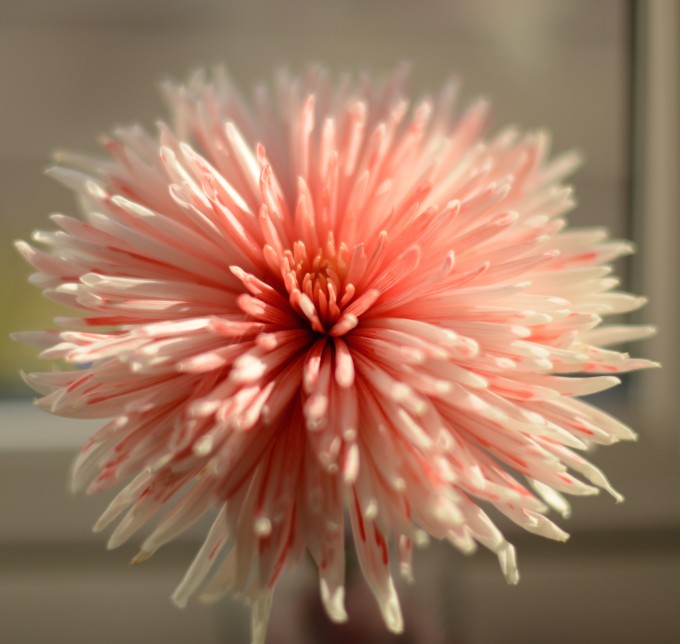
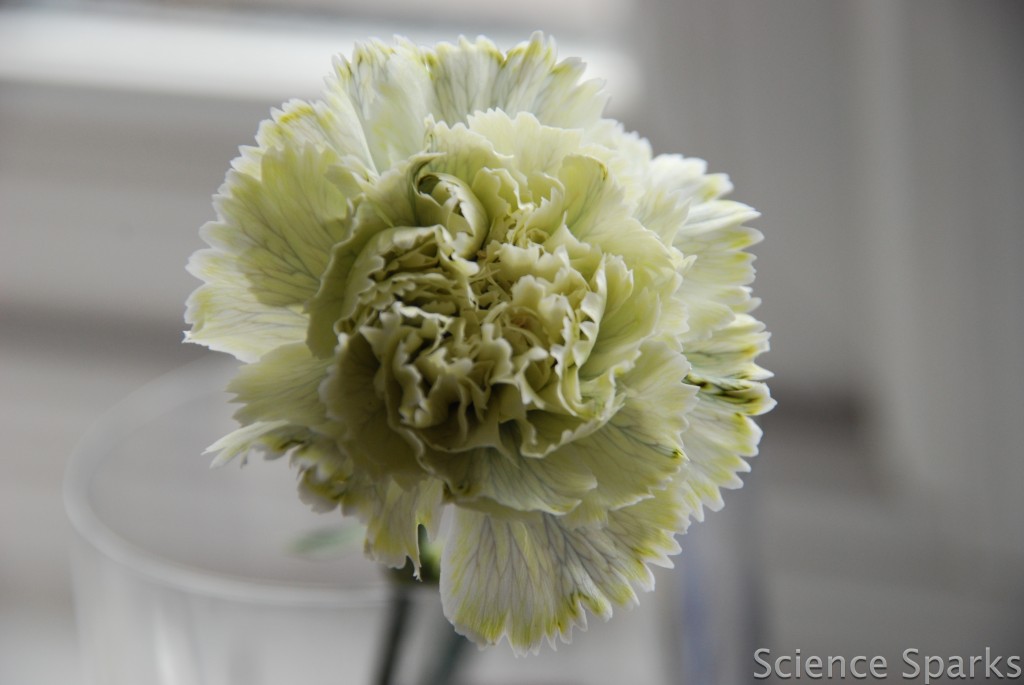
Do you know you can change the colour of white flowers by placing them in a pot of food colouring and water? This easy colour-changing flower science experiment is great for learning about transpiration and transport in plants.
Easy Transpiration Experiment
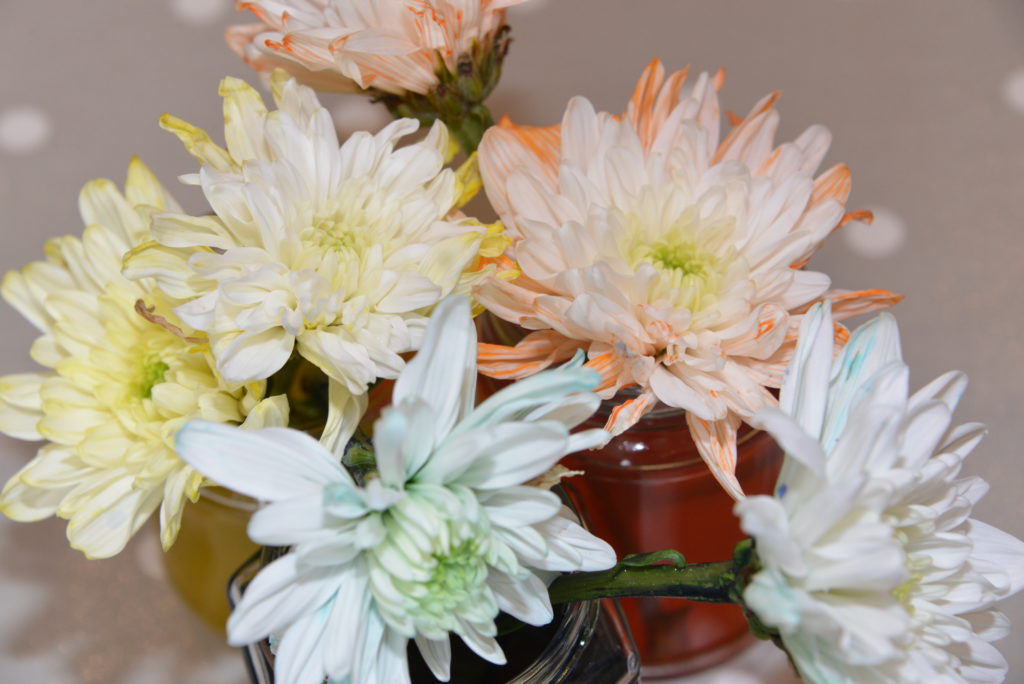

How to make colour-changing flowers
You’ll need
White flowers
Food colouring – we’ve found Wilton gel colours work well. Natural food colourings DO NOT work in our experience.
Water
Small jar or vase
Transpiration experiment – instructions
Trim the flowers at the stalks.
Fill a vase or jar with water and add a little food colouring.
Place the flowers in the jar and leave for a few hours.
Usually, you will see the flowers change colour within a few hours.
Extra Transpiration Challenges
Try carefully splitting a stem in half with a sharp knife ( ask an adult to do this )
Place one half of the stem in one colour water and the other in a different colour. After a few hours, you should have a flower two different coloured petals!
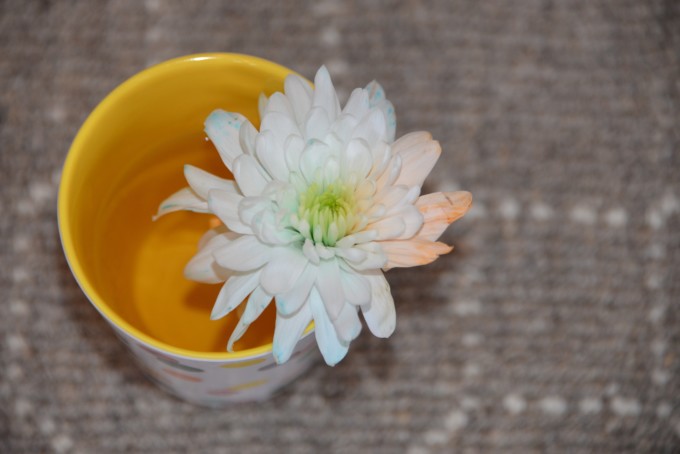

What is Transpiration?
The white petals change colour because of something called the transpiration stream. Transpiration is the movement of water up the stem of a plant from root to leaf when water is lost from the plant due to evaporation and diffusion of water from a plant’s surface. Firstly, water is absorbed by the root and moves through root hair cells via the process of osmosis. It then moves into the xylem vessel, which is the tube that carries the water up the stem. Water moves up the xylem vessel by adhesion (being attracted to the side of the vessel) and cohesion (water molecules being attracted to each other).
When water evaporates from the surface of the leaves, the pressure change pulls the column of water upwards to replace the water lost. There’s a constant transpiration stream of water through the plant.
The best way to consider this is to imagine you have a thick milkshake – the straw can’t carry the milkshake up itself, but if you suck from the top, the milkshake is sucked up the straw. It moves in a column because water molecules are attracted to each other.
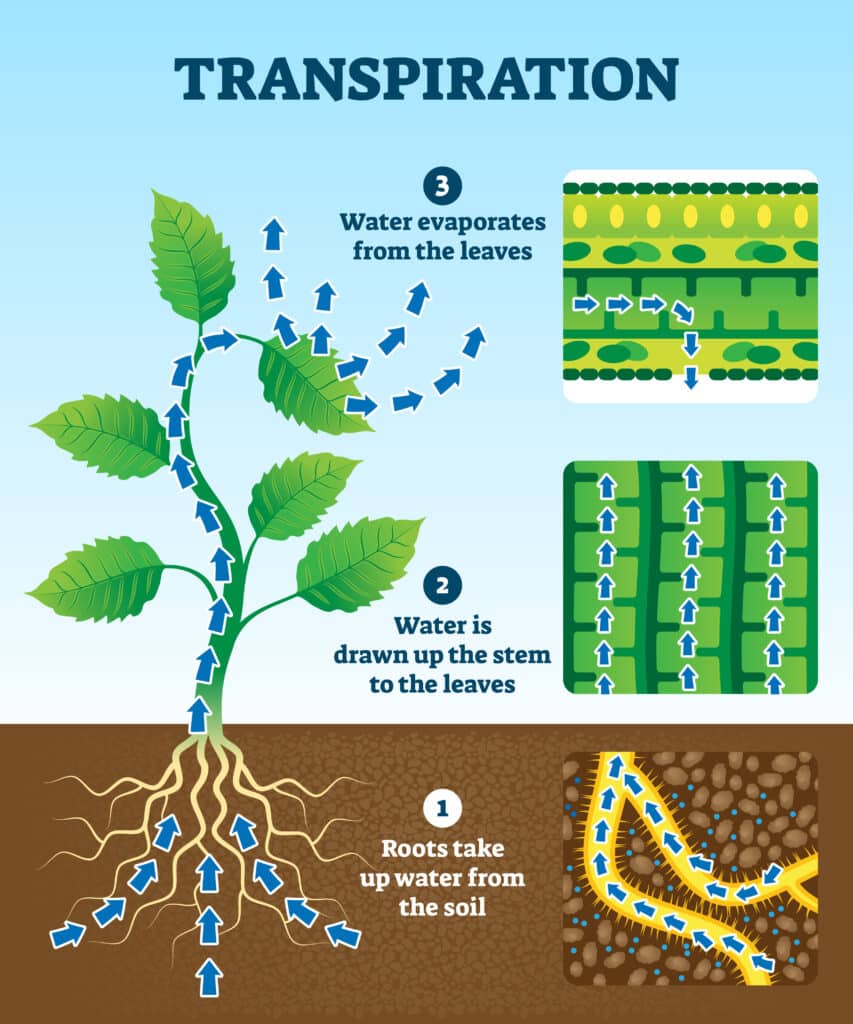
What affects the speed of transpiration?
The rate of transpiration is affected by environmental factors
Factors affecting transpiration
Light
Transpiration is faster when there’s more sunlight. Stomata ( tiny pores on the surface of a plant ) close when it’s dark as they don’t need to be open when photosynthesis is not happening. Photosynthesis also needs sunlight. When the stomata are closed, water cannot escape from the plant’s surface.
Temperature
Transpiration happens at a faster rate in higher temperatures. In warm weather, water particles evaporate and diffuse through the stomata faster, increasing the transpiration rate.
Air movement around the plant
When airflow around a plant is good, transpiration is faster as the water vapour that has just diffused and evaporated from the leaf is moved away, increasing the concentration gradient between the air and the inside of the leaf. Diffusion is faster when the concentration gradient is more significant.
The effect of increasing airflow on the rate of transpiration can be demonstrated using celery, food colouring, water and a hair dryer!
What food colouring should I use?
We have found that natural food colours don’t work, but these Wilton gel colours work every time.
If you liked this experiment, don’t forget to try my other plant science experiments.

Contains Affiliate Links

Last Updated on September 17, 2024 by Emma Vanstone




